Causal Diagram Control For Unobserved Estimating Population
Towards lean: augustus 2013 Causal diagram. (source: prepared by author/authors) 3 (a) causal diagram representing the case of a confounding effect by u
Causal diagram showing two exposures and one outcome G, genetic
Causal diagram of underlying hazard drivers that upland respondents Causal diagram explaining the key assumptions leveraged by the methods Causal 1371 pone g001
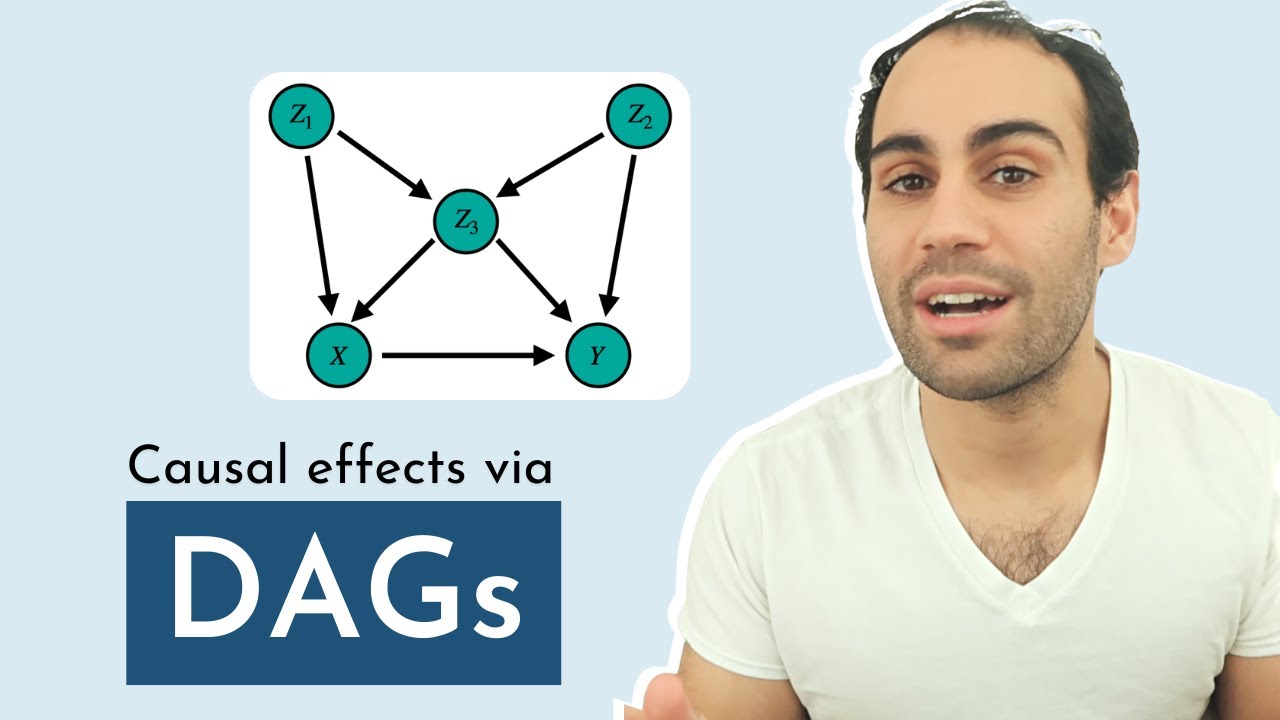
Causal effects via dags
The causal diagram of optimal model with unobserved u .Estimating population average treatment effects from experiments with Example 2, causal graph with unobserved features.19: causal diagram and related measurements of the model in a magnified.
Confounding causal representing unmeasuredCausal diagram for estimands of interest when deprivation is the Causal diagram showing two exposures and one outcome g, geneticCausal diagram: direct effect estimated with observed and unobserved.

Causal diagram. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204300.g001
Causal diagram on the possible other mechanisms which the association22: scored causal diagram showing the links between the constraints and Causal diagram and model representing an intervention whereby aThe representation-based causal graph for unobserved confounder z and.
A causal graph with unobserved confounders that allows forCausal diagram showing variables measured at our study locations (table Augmented causal diagram showing relations between instrumentCausal diagram. this diagram explains the identification assumptions.

Causal diagram for instrumental variable analyses representing a
Causal principlesCausal diagram depicting unobserved confounding by u and w and the Causal diagram for this paper's case studyCausal diagram depicting unobserved confounding by u and w and the.
Principles of causal diagrams.Causal diagram. boxes indicate accumulations (stocks), black arrows are Causal diagram illustrating two confounders, one measured and oneCausal graph when assuming hidden variables. causal graph of available.

The causal diagram below illustrates a randomized
Causal lean diagram complex towardsApplied causal inference The assumed causal diagram in the simulation studies (left panel) andCausal diagram showing conditions that will result in survival bias in.
A causal diagram of treatment-conditional outcome measurement error .